Immunity is like a superhero inside your body, fighting off germs and keeping you healthy. It's a team of cells, tissues, and organs working together to stop bad stuff from making you sick.
Natural immunity is your body's quick and general defense system. It's the first responder that protects you right away from all sorts of germs and keeps them at bay.
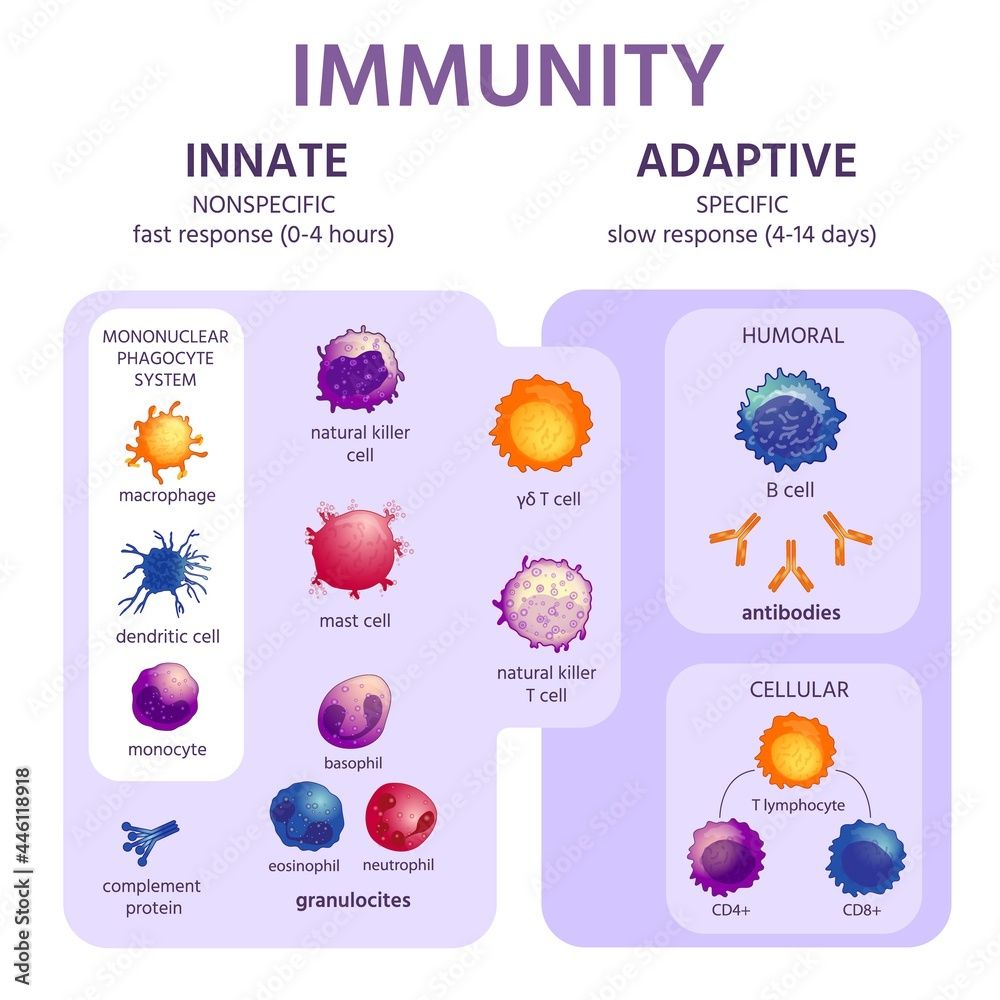
Think of your immune system in two parts - one is quick and general (innate), and the other is like a smart student learning from past experiences (adaptive). Both work together to keep you safe from germs.
The innate immune system is the body's first line of defense against pathogens, responding rapidly and non-specifically to any threat. It includes physical barriers like the skin and mucous membranes, as well as cellular components like neutrophils and macrophages that engulf and destroy pathogens.
In contrast, the adaptive immune system is highly specialized and targeted, adapting its response to specific pathogens encountered by the body. This system involves the production of antibodies by B cells and the activation of T cells, which can recognize and eliminate specific pathogens. What distinguishes the adaptive immune system is its ability to "remember" previous encounters with pathogens, enabling a faster and more efficient response upon subsequent exposures.
Together, these two components of the immune system work synergistically to defend the body against a wide array of infections and maintain overall health.
Two Ways Your Immune System Works
Your immune system has two jobs - one is to defend against anything bad quickly, and the other is to remember what it fought before, so it can do an even better job next time.
These two primary mechanisms are called rapid defense and immunological memory. Its rapid defense mechanisms, primarily governed by the innate immune system, act swiftly and nonspecifically to detect and neutralize pathogens upon initial exposure. This includes physical barriers like the skin, as well as immune cells like neutrophils and macrophages that engulf and destroy invading microbes.
The immune system is capable of immunological memory, characteristic of the adaptive immune response. Through the production of memory cells, such as memory B cells and memory T cells, the immune system "remembers" previous encounters with specific pathogens. Upon re-exposure, these memory cells mount a faster, more robust response, enabling the body to eliminate the threat before it can cause significant harm effectively. Thus, the immune system's dual functions of rapid defense and immunological memory work in tandem to provide comprehensive protection against pathogens and maintain long-term immunity.
A well-balanced diet rich in protein and meat, along with fruits, nuts, and seeds, is crucial for supporting a robust immune system. These foods provide essential nutrients that fortify the body's defenses against infections and diseases. Protein is particularly important, as all immune cells require it to be made. Fruits offer vitamins C and E, along with beta-carotene. Nuts and seeds provide healthy fats, protein, and zinc. Incorporating these foods into your meals promotes optimal immune function and overall well-being.
Immune diseases can be caused by various factors. Genetics plays a significant role, as certain genes can predispose individuals to immune system disorders. Environmental factors, such as exposure to toxins or pollutants, can also contribute. Additionally, infections caused by viruses or bacteria can trigger autoimmune reactions. Another factor is molecular mimicry, where the immune system mistakenly targets normal cells due to similarities with pathogens. Lifestyle factors, such as diet, stress, and sleep, can also impact immune function.
Empty space, drag to resize
The immune system serves as your body's vigilant guardian, constantly surveilling for potential threats and swiftly neutralizing them to maintain your health and well-being. Through a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs, your immune system detects foreign invaders like bacteria, viruses, and parasites, distinguishing them from your body's own cells. Like a diligent bodyguard, it employs a variety of defense mechanisms to eliminate these pathogens, including engulfing them with specialized cells like macrophages, releasing antibodies to tag and neutralize them, and activating killer cells to destroy infected cells. Additionally, the immune system orchestrates inflammatory responses to contain and eliminate pathogens while initiating tissue repair processes to restore health. Through its vigilant surveillance and coordinated actions, the immune system acts as your ultimate protector, tirelessly defending you against harm and ensuring your continued well-being.
In this course, you will learn more about how your immune system spots and fights off germs. It's like having a bodyguard that recognizes trouble and stops it before it can harm you.
Discover the superheroes - vitamin C, D, and zinc - that make your immune system strong. They are like the special foods that keep your body's defenses in top shape.
We’ll also explore common problems like arthritis and allergies that can affect your immune system.
- Arthritis, a condition causing joint inflammation, can lead to pain and stiffness, affecting mobility.
- Allergies occur when the immune system overreacts to harmless substances, resulting in symptoms like sneezing and itching.
- Asthma, marked by airway inflammation and constriction, can cause breathing difficulties.
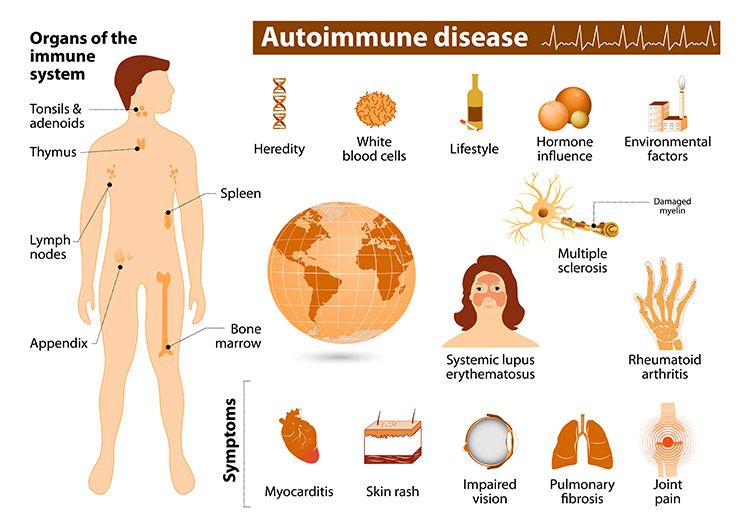
- Autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus involve the immune system attacking the body's tissues, leading to various symptoms.
- Infections such as HIV weaken the immune system, making the body vulnerable to diseases.
Enroll in our immunity course to explore these topics further and learn how to effectively manage these conditions. Know what causes them, what signs to look for, and how they can be managed.
We will talk about some serious illnesses called autoimmune diseases, like multiple sclerosis and lupus. These are tough because your immune system fights against your own body by mistake. Multiple sclerosis messes with your nerves and can make it hard to walk. Lupus can affect different parts of your body, like your skin and joints. Learning about these diseases helps you understand what might happen and how to take care of yourself. It's important to know so you can get help early and feel better. This is just the beginning! In our immunity course, we'll dive even deeper into these topics, providing you with further insights and strategies to enhance your immune health and well-being. Join us on this journey to empower yourself with the knowledge needed to combat health challenges and stay resilient against any threats that may arise.
Immunity is the body's ability to resist and fight off infection or disease.
Natural immunity refers to the immunity that is naturally present in an individual and is not acquired through medical intervention or vaccination.
The immune system is classified into two main categories: the innate immune system and the adaptive (or acquired) immune system.
The two types of immune function are innate immunity, which provides immediate defense against pathogens, and adaptive immunity, which involves a targeted response tailored to specific pathogens.
Foods that help support the immune system include those rich in vitamins C and E, zinc, and antioxidants, such as citrus fruits, berries, nuts, seeds, and leafy green vegetables.
Immune diseases can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, infections, environmental triggers, and autoimmune reactions where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's own tissues.
The immune system protects the body from disease by identifying and destroying pathogens, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites, as well as removing damaged or abnormal cells.
Vitamin C is known to be good for the immune system as it helps support immune cell function and enhances the body's ability to fight off infections.
Five common diseases of the immune system include rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, celiac disease, multiple sclerosis, and inflammatory bowel disease.
The top 5 worst autoimmune diseases, in terms of their impact and severity, are generally considered to be systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), multiple sclerosis (MS), type 1 diabetes, and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).